ECHO course: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
[[Image:echo_heart_parasternal_long_axis.jpg|thumb|Image showing the left parasternal long axis transection (PSLAX) of the heart by the ultrasound waves]] | [[Image:echo_heart_parasternal_long_axis.jpg|thumb|Image showing the left parasternal long axis transection (PSLAX) of the heart by the ultrasound waves]] | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
{| class="wikitable" align="right" width= | {| class="wikitable" align="right" width={{Flashwidth}} | ||
|<flash>file=PSLAX.swf|quality=best|align=center|width={{Flashwidth}}|height={{Flashheight}}|</flash> | |<flash>file=PSLAX.swf|quality=best|align=center|width={{Flashwidth}}|height={{Flashheight}}|</flash> | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 11:17, 3 August 2007
Standard Imaging Planes
Imaging of the heart by means of ultrasound is limited by thoracic anatomy. Air doesn't propagate ultrasound and because of this imaging of the heart is limited to several so-called 'acoustic windows'. These windows are left parasternal, apical, subcostal, suprasternal and right parasternal. Because of the properties of ultrasound intrathoracic fluid (for instance pleural or pericardial effusion) makes imaging easier but more intrathoracic air (COPD) makes imaging more difficult.
Parasternal Imaging Planes
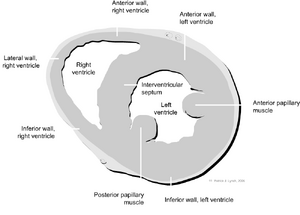
The left parasternal imaging planes are found by placing the transducer in the third or fourth intercostal space on the left of the sternum. There are four standard imaging planes:
- parasternal long axis (PSLAX) and
- three parasternal short axis planes (SAX).
Left parasternal long axis
| quality=best|align=center|width=400|height=200|</flash> |
| enlarge |
Left parasternal short axis