Diastolic Function: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==The Left Ventricle== | ==The Left Ventricle== | ||
There is still much uncertainty about the pathophysiology of diastolic heart failure, | There is still much uncertainty about the pathophysiology of diastolic heart failure, effective treatment has not surfaced yet while it has a similar high mortality and morbidity rate when compared to systolic heart failure. One of the characteristics of diastolic heart failure is an increased LV diastolic stiffness. There are several important measurements echocardiographic measurement to estimate cardiac diastolic performance. | ||
==Left ventricular diastolic function== | ==Left ventricular diastolic function== | ||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
|'''A patient with dyspnea, preserved systolic LV function, dilated left atrium and elevated pulmonary artery systolic pressure, without any significant mitral valve disease that could explain these findings, is the patient that requires an intensified search for diastolic LV dysfunction.''' | |'''A patient with dyspnea, preserved systolic LV function, dilated left atrium and elevated pulmonary artery systolic pressure, without any significant mitral valve disease that could explain these findings, is the patient that requires an intensified search for diastolic LV dysfunction.''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
|align="center" bgcolor="FFFFFF"|[[Image:Diastole. | |align="center" bgcolor="FFFFFF"|[[Image:Diastole.svg]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''I:''' impaired relaxation, '''II:''' moderate diastolic dysfunction (pseudonormal), '''III:''' restrictive left ventricular filling (impaired LV compliance), ECG: electrocardiogram, MI: mitral inflow, MA: mitral annular velocities, PVF: pulmonary venous flow, Vp: velocity of flow progression, LA: left atrium, PASP: pulmonary artery systolic pressure.<cite>2</cite> | |'''I:''' impaired relaxation, '''II:''' moderate diastolic dysfunction (pseudonormal), '''III:''' restrictive left ventricular filling (impaired LV compliance), ECG: electrocardiogram, MI: mitral inflow, MA: mitral annular velocities, PVF: pulmonary venous flow, Vp: velocity of flow progression, LA: left atrium, PASP: pulmonary artery systolic pressure.<cite>2</cite> | ||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! | ! | ||
===Diastolic function flowchart <cite>1</cite>=== | ===Diastolic function flowchart <cite>1</cite>=== | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 115: | Line 116: | ||
#1 pmid=19270053 | #1 pmid=19270053 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
==External links== | |||
* [https://www.techmed.sk/en/echo/diastolic-function/ Diastolic Function - all measurements (TECHmED)] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:07, 9 January 2021
The Left Ventricle
There is still much uncertainty about the pathophysiology of diastolic heart failure, effective treatment has not surfaced yet while it has a similar high mortality and morbidity rate when compared to systolic heart failure. One of the characteristics of diastolic heart failure is an increased LV diastolic stiffness. There are several important measurements echocardiographic measurement to estimate cardiac diastolic performance.
Left ventricular diastolic function
Normal Values diastolic parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement | Age group (y) | ||||
| 16-20 | 21-40 | 41-60 | >60 | ||
| IVRT (ms) | 50 ± 9 (32-68) | 67 ± 8 (51-83) | 74 ± 7 (60-88) | 87 ± 7 (73-101) | |
| E/A ratio | 1.88 ± 0.45 (0.98-2.78) | 1.53 ± 0.40 (0.73-2.33) | 1.28 ± 0.25 (0.78-1.78) | 0.96 ± 0.18 (0.6-1.32) | |
| DT (ms) | 142 ± 19 (104-180) | 166 ± 14 (138-194) | 181 ± 19 (143-219) | 200 ± 29 (142-258) | |
| A duration (ms) | 113 ± 17 (79-147) | 127 ± 13 (101-153) | 133 ± 13 (107-159) | 138 ± 19 (100-176) | |
| PV S/D ratio | 0.82 ± 0.18 (0.46-1.18) | 0.98 ± 0.32 (0.34-1.62) | 1.21 ± 0.2 (0.81-1.61) | 1.39 ± 0.47 (0.45-2.33) | |
| PV Ar (cm/s) | 16 ± 10 (1-36) | 21 ± 8 (5-37) | 23 ± 3 (17-29) | 25 ± 9 (11-39) | |
| PV Ar duration (ms) | 66 ± 39 (1-144) | 96 ± 33 (30-162) | 112 ± 15 (82-142) | 113 ± 30 (53-173) | |
| Septal e´ (cm/s) | 14.9 ± 2.4 (10.1-19.7) | 15.5 ± 2.7 (10.1-20.9) | 12.2 ± 2.3 (7.6-16.8) | 10.4 ± 2.1 (6.2-14.6) | |
| Septal e´/a´ ratio | 2.4* | 1.6 ± 0.5 (0.6-2.6) | 1.1 ± 0.3 (0.5-1.7) | 0.85 ± 0.2 (0.45-1.25) | |
| Lateral e´ (cm/s) | 20.6 ± 3.8 (13-28.2) | 19.8 ± 2.9 (14-25.6) | 16.1 ± 2.3 (11.5-20.7) | 12.9 ± 3.5 (5.9-19.9) | |
| Lateral e´/a´ ratio | 3.1* | 1.9 ± 0.6 (0.7-3.1) | 1.5 ± 0.5 (0.5-2.5) | 0.9 ± 0.4 (0.1-1.7) | |
| |||||
Schematic diastolic filling patterns |
|---|
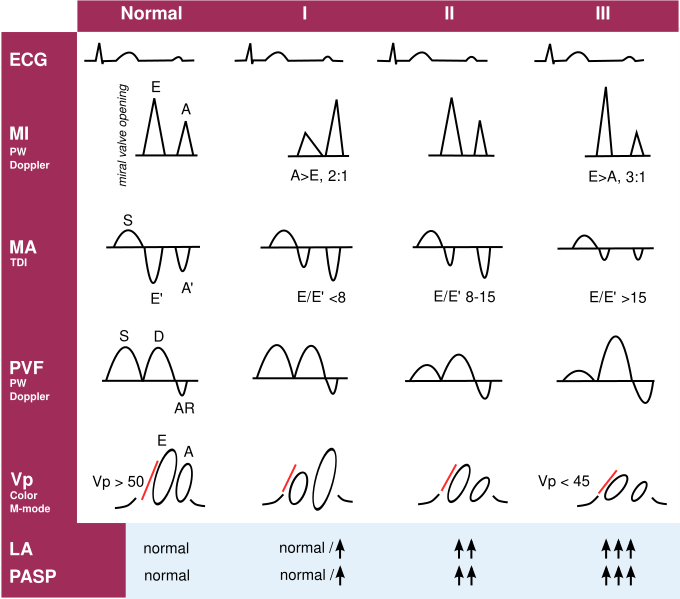
| A patient with dyspnea, preserved systolic LV function, dilated left atrium and elevated pulmonary artery systolic pressure, without any significant mitral valve disease that could explain these findings, is the patient that requires an intensified search for diastolic LV dysfunction. |
|
| I: impaired relaxation, II: moderate diastolic dysfunction (pseudonormal), III: restrictive left ventricular filling (impaired LV compliance), ECG: electrocardiogram, MI: mitral inflow, MA: mitral annular velocities, PVF: pulmonary venous flow, Vp: velocity of flow progression, LA: left atrium, PASP: pulmonary artery systolic pressure.2
Click here for animation on diastolic dysfunction |
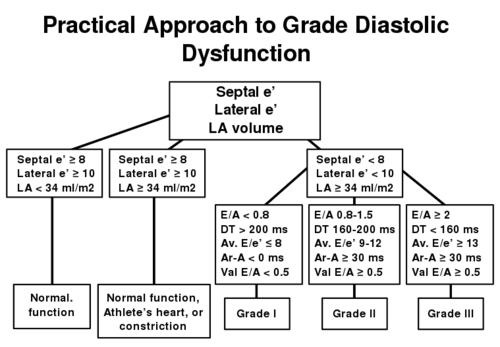
Diastolic function flowchart 1 |
|---|
|
References
<biblio>
- 1 pmid=19270053
</biblio>