Parasternal long axis: Difference between revisions
>Mark No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{auteurs| | {{auteurs| | ||
|mainauthor= [[user:Vdbilt|I.A.C. van der Bilt]] | |mainauthor= [[user:Vdbilt|I.A.C. van der Bilt]] | ||
| Line 5: | Line 4: | ||
|supervisor= | |supervisor= | ||
}} | }} | ||
=Parasternal Long Axis= | |||
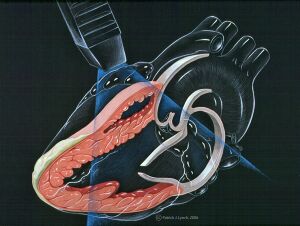
[[Image:echo_heart_parasternal_long_axis.jpg|thumb|Image showing the left parasternal long axis transection (PSLAX) of the heart by the ultrasound waves]] | |||
==Purposes of Getting a Good Parasternal Long Axis (PLAX) View== | |||
Echocardiographic examination of the heart usually begins with a PLAX view. Acquiring a good PLAX view is important to assess left ventricular contractility and to determine the presence of pericardial effusion and right ventricular strain. | |||
==How to Get a Good PLAX View== | |||
To get a good PLAX view, begin with placing the transducer in the third or fourth intercostal space and adjust as necessary, moving a few intercostals spaces up or down. Better results are obtained if the patient is placed in a left lateral decubitus position. This will allow better visualization of the mid-portion and base of the left ventricle, both leaflets of the mitral valve, the aortic valve and the aortic root, the left atrium and the right ventricle. <cite>Nihoyannopoulos</cite> | |||
The transducer is traditionally moved and pointed toward the right shoulder to parallel the beam to the major axis of the left ventricle and to pass it through the center of the left ventricular chamber. Gradual medial to lateral angulation until the left ventricle size is at its maximum will allow one to see the minor axis at its maximal state and the mitral valve leaflet excursion at its greatest. Minor axis dimensions may then be viewed and recorded. | |||
==Characteristics of a Good PLAX View== | |||
One will be able to know of a good PLAX view is taken when the septum is oriented almost horizontally, clearly delineating between the left and right side of the heart, and the apex of the of the left ventricle and the tricuspid valve are not visualized. The mitral and aortic valves, however, should be visible. | |||
==Structures that can be seen in the PLAX view== | |||
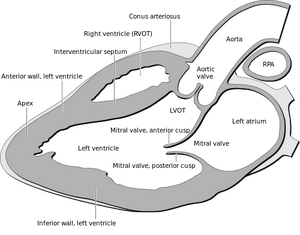
[[Image:Heart_normal_lpla_echo_view.png|thumb|Schematic diagram of the different structures seen in a good PLAX view.]] | |||
*Right ventricle | |||
*Left ventricle | |||
*Mitral valve | |||
*Left atrium | |||
*Descending aorta | |||
*Aortic valve | |||
*Aortic root | |||
*Pericardium | |||
*Right ventricular inflow and outflow tracts | |||
{{clr}} | |||
==2D Echo Measurements== | |||
Majority of measurements are done with 2D echo imaging. Once the best diastolic frame having the largest left ventricular cavity is chosen, septal and posterior wall thickness, left ventricular diastolic cavity, and aortic root diameter can be determined. Use a systolic frame to measure the dimensions of the left ventricle and the left atrial diameter. | |||
==M-Mode Echo Measurement== | |||
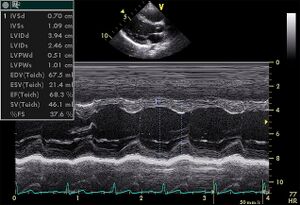
[[Image:PLAX_Mmode.jpg|thumb|alt=Alt text|Image showing the left parasternal long axis transection (PSLAX) of the heart by M-mode imaging.]] | |||
Determining left ventricular dimensions and ejection fraction are few of the cases wherein M-mode imaging is used. It is one-dimensional and usually relies on the correct alignment of the M-mode along the left ventricle. | |||
==Using Color Doppler Ultrasound== | |||
It is sometimes necessary to use color Doppler ultrasound when valvular regurgitation is suspected, although this method should not be used to as the final diagnostic tool to determine valve dysfunction as the Doppler beam is nearly perpendicular to the flow. Instead, the presence of valvular regurgitation is based on the cardiac cycle, not the color-coding.<cite>Feigenbaum1</cite> | |||
==Example== | ==Example== | ||
This a parasternal long axis view of a normal heart. | This a parasternal long axis view of a normal heart. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 44: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
==References== | |||
<biblio> | |||
#Nihoyannopoulos isbn=1848822928 | |||
#Feigenbaum1 isbn=0781795575 | |||
</biblio> | |||
Revision as of 11:13, 29 January 2012
| Author | I.A.C. van der Bilt | |
| Moderator | I.A.C. van der Bilt | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
Parasternal Long Axis
Purposes of Getting a Good Parasternal Long Axis (PLAX) View
Echocardiographic examination of the heart usually begins with a PLAX view. Acquiring a good PLAX view is important to assess left ventricular contractility and to determine the presence of pericardial effusion and right ventricular strain.
How to Get a Good PLAX View
To get a good PLAX view, begin with placing the transducer in the third or fourth intercostal space and adjust as necessary, moving a few intercostals spaces up or down. Better results are obtained if the patient is placed in a left lateral decubitus position. This will allow better visualization of the mid-portion and base of the left ventricle, both leaflets of the mitral valve, the aortic valve and the aortic root, the left atrium and the right ventricle. Nihoyannopoulos The transducer is traditionally moved and pointed toward the right shoulder to parallel the beam to the major axis of the left ventricle and to pass it through the center of the left ventricular chamber. Gradual medial to lateral angulation until the left ventricle size is at its maximum will allow one to see the minor axis at its maximal state and the mitral valve leaflet excursion at its greatest. Minor axis dimensions may then be viewed and recorded.
Characteristics of a Good PLAX View
One will be able to know of a good PLAX view is taken when the septum is oriented almost horizontally, clearly delineating between the left and right side of the heart, and the apex of the of the left ventricle and the tricuspid valve are not visualized. The mitral and aortic valves, however, should be visible.
Structures that can be seen in the PLAX view
- Right ventricle
- Left ventricle
- Mitral valve
- Left atrium
- Descending aorta
- Aortic valve
- Aortic root
- Pericardium
- Right ventricular inflow and outflow tracts
2D Echo Measurements
Majority of measurements are done with 2D echo imaging. Once the best diastolic frame having the largest left ventricular cavity is chosen, septal and posterior wall thickness, left ventricular diastolic cavity, and aortic root diameter can be determined. Use a systolic frame to measure the dimensions of the left ventricle and the left atrial diameter.
M-Mode Echo Measurement
Determining left ventricular dimensions and ejection fraction are few of the cases wherein M-mode imaging is used. It is one-dimensional and usually relies on the correct alignment of the M-mode along the left ventricle.
Using Color Doppler Ultrasound
It is sometimes necessary to use color Doppler ultrasound when valvular regurgitation is suspected, although this method should not be used to as the final diagnostic tool to determine valve dysfunction as the Doppler beam is nearly perpendicular to the flow. Instead, the presence of valvular regurgitation is based on the cardiac cycle, not the color-coding.Feigenbaum1
Example
This a parasternal long axis view of a normal heart.
| <flash>file=PLAXnormal.swf |
| A parasternal long axis |
References
<biblio>
- Nihoyannopoulos isbn=1848822928
- Feigenbaum1 isbn=0781795575
</biblio>