Cardiomyopathy: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Click [http://www.cardiogenetica.nl/index.php?menuID=2 '''here'''] for detailed information on various cardiomyopathy | Click [http://www.cardiogenetica.nl/index.php?menuID=2 '''here'''] for detailed information on various cardiomyopathy. | ||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | {| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | ||
|+ Listed below are the main disorders and their characteristics with examples.<cite>1</cite> | |||
|- | |- | ||
!Condition | !Condition | ||
!Features | !Features | ||
!Example | !Example | ||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
!rowspan="4" valign="top"|Arrythmogene right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) | !rowspan="4" valign="top"|Arrythmogene right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) | ||
|rowspan="4" valign="top"| | |rowspan="4" valign="top"| | ||
*Fibrofatty degeneration of the RV . | *Fibrofatty degeneration of the RV. | ||
*Myocardial degeneration leads to RV dilation and poor RVF . | *Myocardial degeneration leads to RV dilation and poor RVF. | ||
*Ventricular fibrillation by slow conduction velocities , guide block and spatial variation in conduction velocity . | *Ventricular fibrillation by slow conduction velocities, guide block and spatial variation in conduction velocity. | ||
*Aneurysms of the RV free wall . | *Aneurysms of the RV free wall. | ||
* | *Echodense moderator band and myocardial RV free wall. | ||
*Genetic component | *Genetic component | ||
*Rare 1 : 5000 people. | *Rare 1:5000 people. | ||
|Video | |Video | ||
|- | |- | ||
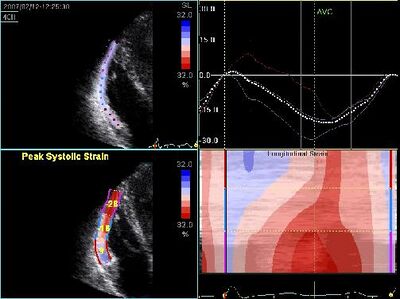
| Line 47: | Line 48: | ||
!Decreased RV strain in ARVC | !Decreased RV strain in ARVC | ||
|- | |- | ||
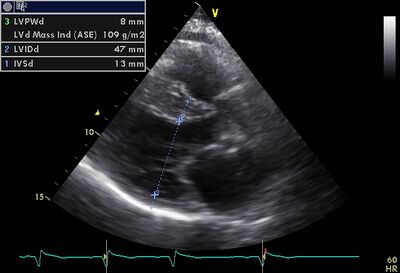
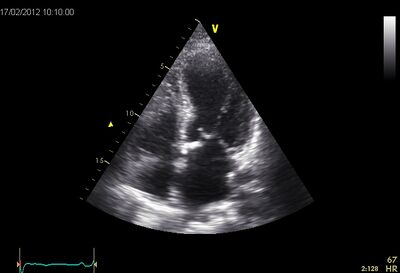
!rowspan="6" valign="top"|Dilated cardiomyopathy ( DCM ) | !rowspan="6" valign="top"|Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) | ||
|rowspan="6" valign="top"| | |rowspan="6" valign="top"| | ||
*It is the most common form of cardiomyopathy. | *It is the most common form of cardiomyopathy. | ||
*Also known as congestive cardiomyopathy | *Also known as congestive cardiomyopathy. | ||
*Poor LVF and LV dilatation. | *Poor LVF and LV dilatation. | ||
*Arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation 20-30%). | *Arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation 20-30%). | ||
*Clot formation, which may lead to thrombo-embolic complications. | *Clot formation, which may lead to thrombo-embolic complications. | ||
*Often accompanied by pulmonary hypertension, dilation of other compartments, and an insufficiency of mitral and / or tricuspid valve | *Often accompanied by pulmonary hypertension, dilation of other compartments, and an insufficiency of mitral and/or tricuspid valve | ||
*Familial DCM's common to autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive and sex-linked inheritance. | *Familial DCM's common to autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive and sex-linked inheritance. | ||
*Causes: | *Causes: | ||
**(post-) infectious: various viruses and bacteria, as the final stage of myocarditis. | **(post-) infectious: various viruses and bacteria, as at the final stage of myocarditis. | ||
**intoxication: cocaine, alcohol abuse. | **intoxication: cocaine, alcohol abuse. | ||
**iatrogenic: some chemostatica, X-ray radiation. | **iatrogenic: some chemostatica, X-ray radiation. | ||
**Metabolic: vitamin B1 deficiency. | **Metabolic: vitamin B1 deficiency. | ||
**-idiopathic: In approximately 30% of cases, no cause is found | **-idiopathic: In approximately 30% of cases, no cause is found | ||
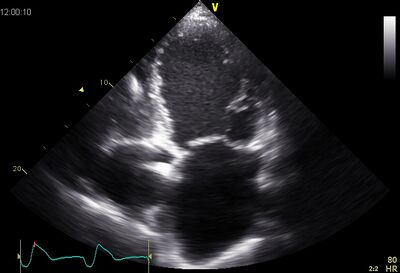
|[[Image:DCM01.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
!Dilated LV on AP4CH | |||
|- | |- | ||
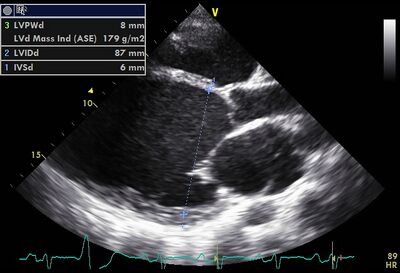
|[[Image:LVF slecht05.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
!Dilated LV on PLAX | |||
|- | |- | ||
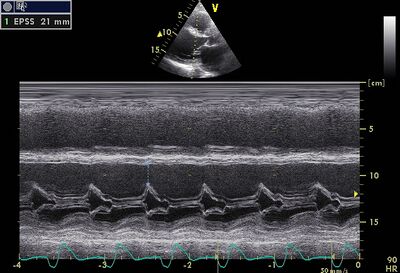
|[[Image:EPSS01.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
!EPSS is a useful measurement to follow up DCM | |||
|- | |- | ||
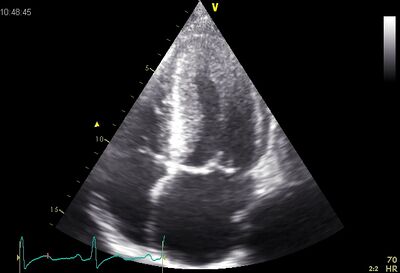
| | !rowspan="6" valign="top"|Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) | ||
|rowspan="6" valign="top"| | |||
*65% asymmetric hypertrophy of the myocardium, usually ventricular septum sometimes apical involvement. | |||
*35% symmetrical hypertrophy of the myocardium (not to be confused with aortic stenosis or hypertension). | |||
*Small LV lumen. | |||
*Preserved systolic LV function (EF normal or slightly decreased) | |||
*Diastolic dysfunction. | |||
*Autosomal dominant progressive deviation from nature. | |||
*Could be associated with sudden cardiac death due to ventricular fibrillation, an increased risk of thromboembolism. | |||
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy ( HCM ) | *Heart failure can be caused by the rigidity of the thickened heart muscle (diastolic heart failure), by an obstruction in the LVOT (SAM) and is associated with mitral valvular insufficiency. The course of the disease is progressive. | ||
*Occurs in persons 1:500-1000 | |||
65% | |[[Image:Asym.cmp1.jpg|400px]] | ||
35 % | |- | ||
Small LV lumen . | !Asymmetric hypertrophy | ||
Preserved systolic LV function ( EF normal or slightly decreased) | |- | ||
Diastolic dysfunction . | |[[Image:HCM01.jpg|400px]] | ||
Autosomal dominant progressive deviation from nature . | |- | ||
!Symmetrical hypertrophy | |||
Heart failure can be caused by the rigidity of the thickened heart muscle ( diastolic heart failure ) , by an obstruction in the LVOT (SAM ) is associated with mitral valvular insufficiency . The course of the disease is progressive . | |- | ||
Occurs in persons 1:500-1000 | |[[Image:ApicHCM.jpg|400px]] | ||
|- | |||
!Apical hypertrophy | |||
|- | |||
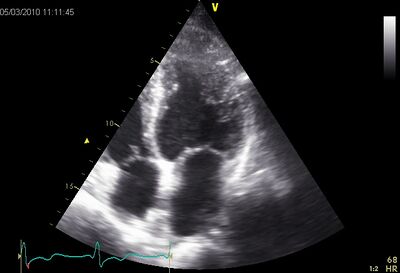
!rowspan="4" valign="top"|Non-compaction cardiomyopathy (NCCMP) | |||
|rowspan="4" valign="top"| | |||
*LV wall has a spongy appearance. | |||
Non - compaction cardiomyopathy ( NCCMP ) | *Jenni criteria (Heart 2007). | ||
*Also called insulated non compaction of the ventricular myocardium (INVM), it is a rare form of congenital heart disease in which the tissue of the ventricular myocardium is not well constructed in terms of texture. | |||
*After HCM DCM, it is the most common cause of primary cardiomyopathy in children. | |||
Jenni criteria ( Heart 2007) . | *It is a congenital defect, which occurs in the 20th week of pregnancy. | ||
Also called insulated non compaction of the ventricular myocardium ( INVM ) , is a rare form of congenital heart disease in which the tissue of the ventricular myocardium is constructed in terms of texture | *The condition is expressed by heart failure, arrhythmias, and an increased risk of thrombus formation. | ||
*The disorder often manifests itself later in life and has a high mortality rate due to heart failure and arrhythmias. | |||
It is a congenital defect , which occurs in the 20th week of pregnancy . | |[[Image:NCCMP02.jpg|400px]] | ||
The condition is expressed by heart failure, arrhythmias, and an increased risk of thrombus formation. | |- | ||
The disorder often manifests itself later in life and has a high mortality rate due to heart failure and arrhythmias . | !NCCMP with crypts and apical midventriculair | ||
|- | |||
NCCMP with crypts and apical midventriculair | |Video | ||
|- | |||
NCCCMP on PSax | !NCCCMP on PSax | ||
|- | |||
!rowspan="2" valign="top"|Restrictive cardiomyopathy | |||
|rowspan="2" valign="top"| | |||
Stiffened myocardium. | *Stiffened myocardium. | ||
This form comes after at least 1 and is usually associated with storage diseases , such as sarcoidosis , amyloidosis , and the like. | *This form comes after at least 1 and is usually associated with storage diseases, such as sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, and the like. | ||
Preserved systolic LVF . LV is not dilated . | *Preserved systolic LVF. LV is not dilated. | ||
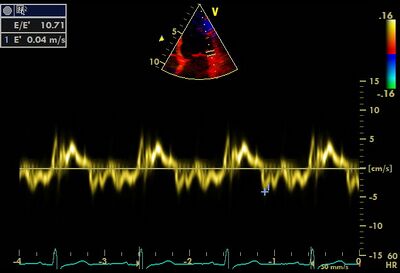
Diastolic dysfunction ( see fig.) | *Diastolic dysfunction (see fig.) | ||
LV and RV may be hypertrophied . | *LV and RV may be hypertrophied. | ||
Dilated atria and VCI . | *Dilated atria and VCI. | ||
Pulmonary hypertension . | *Pulmonary hypertension. | ||
Myocardial echo during and amyloidosis speckled | *Myocardial echo during and amyloidosis speckled | ||
|[[Image:Restrcmp.jpg|400px]] | |||
Abnormally low É in restrictive | |- | ||
Tako- tsubo cardiomyopathy | !Abnormally low É in restrictive cardiomyopathy | ||
|- | |||
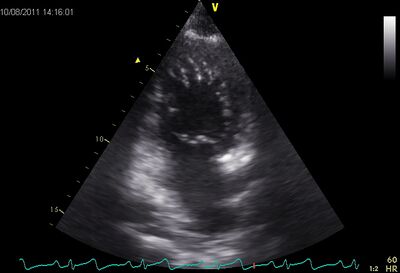
Apical ballooning , | !rowspan="2" valign="top"|Tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy | ||
|rowspan="2" valign="top"| | |||
Is more common in women than in men , the average age of 62 to 75 years . | *Takotsubo is named after the ceramic pots used to trap octopus in Japan. | ||
*Apical ballooning, akinetic of the apex. This gives the LV the octupus trap shape. | |||
Also called "broken heart syndrome" or " Stress CMP " | *Manifests itself as an acute myocardial infarction with ST elevations, however, no significant coronary artery disease. | ||
LV | *Is more common in women than in men, the average age of 62 to 75 years. | ||
*Stress induced, is triggered by an acute illness or intense emotional or physical stress | |||
Apical ballooning | *Also called "broken heart syndrome" or "Stress CMP". | ||
*LV normalizes in a few days to several weeks. | |||
|[[Image:TakoTsubo01.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |||
!Apical ballooning | |||
|} | |} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
#1 | #1 [http://www.uptodate.com/contents/echocardiographic-recognition-of-cardiomyopathies?source=search_result&search=cardiomyopathy+echo&selectedTitle=1~150| Echocardiographic | ||
#2 recognition of cardiomyopathies] | |||
#3 [https://vetocorleone.com/download-idn-poker/ Download IDN Poker APk] | |||
#4 [https://vetocorleone.com/deposit-idn-poker/ Deposit IDNPoker Terbaru] | |||
#5 [https://vetocorleone.com/daftar-idn-poker/ Daftar IDN Poker Online] | |||
#6 [https://vetocorleone.com/ IDN Poker] | |||
#7 [https://daftar-idn-poker88.wildapricot.org/ IDN Poker] | |||
#8 [https://togelonlineku3.wildapricot.org/ Togel Hongkong] | |||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
Latest revision as of 04:33, 15 June 2021
Cardiomyopathy (CMP) is a collective term for various diseases of the heart muscle (myocardium). For various reasons, the function of the myocardium decreased (see table). The different variants of a CMP are generally classified on the basis of echocardiographic characteristics.
| LV function decline in most common cardiomyopathy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Systolic function | Diastolic Function | |
| Dilated CMP | ↓ | =/↓ |
| Hypertrophic CMP | ↑ | ↓ |
| Restrictive CMP | = | ↓ |
Click here for detailed information on various cardiomyopathy.
References
<biblio>
- 1 [http://www.uptodate.com/contents/echocardiographic-recognition-of-cardiomyopathies?source=search_result&search=cardiomyopathy+echo&selectedTitle=1~150%7C Echocardiographic
- 2 recognition of cardiomyopathies]
- 3 Download IDN Poker APk
- 4 Deposit IDNPoker Terbaru
- 5 Daftar IDN Poker Online
- 6 IDN Poker
- 7 IDN Poker
- 8 Togel Hongkong
</biblio>