Art Valves: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | {| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Image: | |[[Image:Klep_profiel_v2.svg|400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Valve profile in different types of mechanical prosthetic valves | !Valve profile in different types of mechanical prosthetic valves | ||
| Line 147: | Line 147: | ||
Surgical replacement of the aortic valve is an effective treatment modality for patients with degenerative aortic stenosis and calcification. In an aging population, however, there are more and more patients in whom surgery poses a high risk. Due to recent developments, there is a less invasive alternative possible, resulting in a prosthesis (bioprosthesis) of the aorta, through the femoral artery or transapical can be inserted. | Surgical replacement of the aortic valve is an effective treatment modality for patients with degenerative aortic stenosis and calcification. In an aging population, however, there are more and more patients in whom surgery poses a high risk. Due to recent developments, there is a less invasive alternative possible, resulting in a prosthesis (bioprosthesis) of the aorta, through the femoral artery or transapical can be inserted. | ||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0 | {| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Image:Edw sapien.gif| | |[[Image:Edw sapien.gif|200px]] | ||
|[[Image:Med corevalve.png| | |[[Image:Med corevalve.png|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Edwards Sapien<cite>2</cite> | !Edwards Sapien<cite>2</cite> | ||
| Line 160: | Line 160: | ||
Preoperative [[Aorta|aortic dimensions]] is all well mapped with an echocardiographic examination, so that the interventional cardiologist knows exactly where the implant is to be placed.<cite>3</cite> | Preoperative [[Aorta|aortic dimensions]] is all well mapped with an echocardiographic examination, so that the interventional cardiologist knows exactly where the implant is to be placed.<cite>3</cite> | ||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0 | {| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Image:Med-corevalve2. | |[[Image:Med-corevalve2.svg|300px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 172: | Line 172: | ||
|Video | |Video | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Paravalvular leakage | !colspan="2"|Paravalvular leakage | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 09:39, 2 April 2014
Different types of valve art
Before starting with echocardiographic evaluation of a valve prosthesis it is necessary to be aware of the different types of valve prostheses. There is a difference in the kind and in the type and diameter. Thus, each manufacturer has its own characteristics. And there is a difference in whether the prosthesis is biologically or mechanically created.
Click here for normal mechanical prosthesis
Click here for normal biological prostheses

|
| Mechanical prosthetic valves |
|---|
| Advantages and disadvantages of mechanical and bioprosthetic | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Biological | |
| Advantages |
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
| NB: For all valve prostheses is indicated in some cases endocarditis prophylaxis.1 | ||
Types of mechanical prosthetic valves
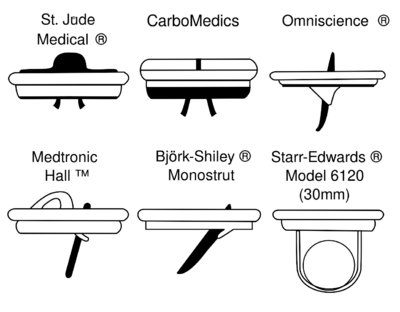
|
| Valve profile in different types of mechanical prosthetic valves |
|---|
Features of the different prosthetic
| Type of prosthetic valve1 | Brand | Obstruction | Leakage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ball in Cage |
|
Many | Little |
| Tilting disc |
|
Little | Many |
| Bileaflet |
|
Little | Many |
| Homograft |
|
No | No |
| Unstented bioprosthesis |
|
No | No |
| Stented bioprosthesis |
|
Many | No |
Postoperative ultrasound
After valve replacement have to be at the time that a patient is stable (hemodynamic and metabolism, "no anemia") to be an output echo is made for capturing of valve parameters. Here it is to calculate with use of the art valve diameter, a valve surface is important so that a size is recorded regardless of the cardiac output. (Fever creates a hyperdynamic circulation so the gradients will increase, not the calculated valve area).
Bioprostheses also have their own characteristics that must be recorded postoperatively. Every patient has some hi-profile bioprostheses the struts and the structure of the stabbing valve in the outflow tract. It may be some LV outflow obstruction occur. The main problem with bioprostheses is the degeneration. This can be both progressive obstruction occur as tearing of leaflets which there is a major failure occurs.
| Data needed for evaluation of mitral prosthetic valve | Data needed for evaluation of aortic prosthetic valve |
|---|---|
| Maximum and mean gradient | Maximum and mean gradient |
| MVA calculated with VTI MV, VTI LVOT + LVOT diameter | AVA calculated with VTI Ao, LVOT VTI, valve size to use for LVOT diameter |
| Pressure halftime | Para valvular aoi |
| Scanning valve ring para valvular leakage | Fistulas, abscesses |
| Video | Video |
| Too much mobility MKV | Resulting in serious leakage MKV |
|---|
Percutaneous Aortic Valve
Surgical replacement of the aortic valve is an effective treatment modality for patients with degenerative aortic stenosis and calcification. In an aging population, however, there are more and more patients in whom surgery poses a high risk. Due to recent developments, there is a less invasive alternative possible, resulting in a prosthesis (bioprosthesis) of the aorta, through the femoral artery or transapical can be inserted.
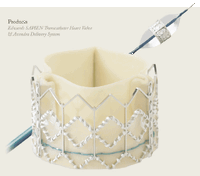
|

|
| Edwards Sapien2 | Medtronic Core Valve3 |
|---|
Echocardiogafie in percutaneous aortic valve
Preoperative aortic dimensions is all well mapped with an echocardiographic examination, so that the interventional cardiologist knows exactly where the implant is to be placed.3
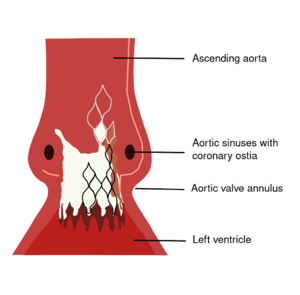
|
Postoperatively is always an echocardiographic examination is necessary to exclude paravalvular leakage. Shortly after placement of a percutaneous valve is almost inevitable that there paravalvular leak is present because the aortic wall where the prosthesis against them is not smooth and round but rough and irregular. A slight paravalvular leakage is still accepted and usually disappears after a few weeks if tissue has grown over the prosthesis. In severe paravalvular leakage is the probability that the prosthesis becomes loose it big so it must be replaced.
| Video | Video |
| Paravalvular leakage | |
|---|---|
References
<biblio>
- 1 R.B.A, van den Brink ‘Kunstkleppen' in "Praktische echocardiografie",Hamer, J.P.M, Pieper P.G, et al, 2e druk, 2009, Houten, Bohn Stafleu van Loghum, DOI: 10.1007/978-90-313-7565-3_9, Print ISBN: 978-90-313-6235-6
- 2 Edwards SAPIEN Transcatheter Heart Valve & Ascendra Delivery System
- 3 The CoreValve ® transcatheter-heart valve
</biblio>