Pulmonary Hypertension: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
Pulmonary hypertension is a rare cause of high blood pressure(hypertension) in the pulmonary artery(pulmonary artery). When the blood vessels of the lungs becomes damaged, such as in pulmonary arterial hypertension, the thickening and stiffening of the pulmonary artery walls occur which causes deviations in the vessel wall. The consequence of this is that the pressure in the pulmonary artery rises and also in the RV. PH is a pressure load on the right heart. Click [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ROz1XSWwxR4 '''here'''] to see an animation about PH. | Pulmonary hypertension is a rare cause of high blood pressure (hypertension) in the pulmonary artery (pulmonary artery). When the blood vessels of the lungs becomes damaged, such as in pulmonary arterial hypertension, the thickening and stiffening of the pulmonary artery walls occur which causes deviations in the vessel wall. The consequence of this is that the pressure in the pulmonary artery rises and also in the RV. PH is a pressure load on the right heart. Click [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ROz1XSWwxR4 '''here'''] to see an animation about PH. | ||
==WHO classification== | ==WHO classification== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
!Subcategories | !Subcategories | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension(PAH) | !valign="top"|Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension(PAH) | ||
| | | | ||
*Idiopathic PAH(unknown cause) | *Idiopathic PAH(unknown cause) | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
*Persistent pulmonary hypertension of newborn | *Persistent pulmonary hypertension of newborn | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Pulmonary hypertension with left heart disease | !valign="top"|Pulmonary hypertension with left heart disease | ||
| | | | ||
*In disorders of left atrium and ventricle | *In disorders of left atrium and ventricle of the heart | ||
of the heart | |||
*With Valvular | *With Valvular | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Pulmonary hypertension in pulmonary disease and/or hypoxemia | !valign="top"|Pulmonary hypertension in pulmonary disease and/or hypoxemia | ||
| | | | ||
*Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD) | *Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD) | ||
*Interstitial lung disease | *Interstitial lung disease | ||
*Sleep disorders, alveolar hypoventilation; | *Sleep disorders, alveolar hypoventilation; chronic exposure to high altitude | ||
chronic exposure to high altitude | |||
*Congenital malformations/developmental | *Congenital malformations/developmental | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Pulmonary hypertension due to chronic thrombotic and/or embolic processes | !valign="top"|Pulmonary hypertension due to chronic thrombotic and/or embolic processes | ||
| | | | ||
*Thromboembolic obstruction of proximal pulmonary arteries | *Thromboembolic obstruction of proximal pulmonary arteries | ||
| Line 40: | Line 38: | ||
*Embolism of the lung (eg: tumor, parasites, foreign body, bone marrow) | *Embolism of the lung (eg: tumor, parasites, foreign body, bone marrow) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Pulmonary hypertension as a result of other diseases and disorders | !valign="top"|Pulmonary hypertension as a result of other diseases and disorders | ||
| | | | ||
*Sarcoidosis | *Sarcoidosis | ||
| Line 60: | Line 58: | ||
!Likely | !Likely | ||
|- | |- | ||
!SPAP | |||
|<36 mmHg | |align="center"|<36 mmHg | ||
|36-50 mmHg | |align="center"|36-50 mmHg | ||
|>50 mmHg | |align="center"|>50 mmHg | ||
|- | |- | ||
!TR Vmax | |||
|<2.8 m/s | |align="center"|<2.8 m/s | ||
|2.9-3.4 m/s | |align="center"|2.9-3.4 m/s | ||
|>3.4 m/s | |align="center"|>3.4 m/s | ||
|- | |- | ||
!AccT | |||
|>120 ms | |align="center"|>120 ms | ||
|120-60 ms | |align="center"|120-60 ms | ||
|<60 ms | |align="center"|<60 ms | ||
|- | |- | ||
!RV MPI (TCO-ET/ET) | |||
|<0.36 | |align="center"|<0.36 | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
!RV MPI (TDI) | |||
|<0:50 | |align="center"|<0:50 | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 93: | Line 91: | ||
!Formula | !Formula | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Systolic PA pressure | |||
Diastolic PA pressure 4 x(PR Ved) | |4 x(TR Vmax)<sup>2</sup> + estimated RA pressure | ||
Mean PA pressure 0.3 x systolic PA pressure + 0.6 x diastolic PA pressure | |- | ||
90 - (0.62 x ACCT) if Acct < 120ms | !Diastolic PA pressure | ||
4 x(PR Vmax) | |4 x(PR Ved)<sup>2</sup> + estimated RA pressure | ||
TR PGmean + estimated RA pressure | |- | ||
!rowspan="4" valign="top"|Mean PA pressure | |||
|0.3 x systolic PA pressure + 0.6 x diastolic PA pressure | |||
|- | |||
|90 - (0.62 x ACCT) if Acct < 120ms | |||
|- | |||
|4 x(PR Vmax)<sup>2</sup> + estimated RA pressure | |||
|- | |||
|TR PGmean + estimated RA pressure | |||
|} | |} | ||
==Examples of severe pulmonary hypertension<cite>1</cite>== | |||
Short | {| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | ||
|- | |||
Increased Systolic PA pressure Increased MPI, extension of isovolumetric times | |[[Image:PVAccT02.jpg|400px]] | ||
|Video | |||
|- | |||
!Short AccT with "systolic notch" | |||
!Flattened septum | |||
|- | |||
|[[Image:SPAP01.jpg|400px]] | |||
|[[Image:PAH01.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |||
!Increased Systolic PA pressure | |||
!Increased MPI, extension of isovolumetric times | |||
|} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
#1 pmid= | #1 pmid=22941889 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
Latest revision as of 21:55, 7 February 2014
Pulmonary hypertension is a rare cause of high blood pressure (hypertension) in the pulmonary artery (pulmonary artery). When the blood vessels of the lungs becomes damaged, such as in pulmonary arterial hypertension, the thickening and stiffening of the pulmonary artery walls occur which causes deviations in the vessel wall. The consequence of this is that the pressure in the pulmonary artery rises and also in the RV. PH is a pressure load on the right heart. Click here to see an animation about PH.
WHO classification
Pulmonary hypertension is classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as the place where the obstruction lies.
| Classification | Subcategories |
|---|---|
| Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension(PAH) |
|
| Pulmonary hypertension with left heart disease |
|
| Pulmonary hypertension in pulmonary disease and/or hypoxemia |
|
| Pulmonary hypertension due to chronic thrombotic and/or embolic processes |
|
| Pulmonary hypertension as a result of other diseases and disorders |
|
Evidence of pulmonary hypertension
| Unlikely | Possible | Likely | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPAP | <36 mmHg | 36-50 mmHg | >50 mmHg |
| TR Vmax | <2.8 m/s | 2.9-3.4 m/s | >3.4 m/s |
| AccT | >120 ms | 120-60 ms | <60 ms |
| RV MPI (TCO-ET/ET) | <0.36 | ||
| RV MPI (TDI) | <0:50 |
Calculations for estimating pressure in the pulmonary artery
| Formula | |
|---|---|
| Systolic PA pressure | 4 x(TR Vmax)2 + estimated RA pressure |
| Diastolic PA pressure | 4 x(PR Ved)2 + estimated RA pressure |
| Mean PA pressure | 0.3 x systolic PA pressure + 0.6 x diastolic PA pressure |
| 90 - (0.62 x ACCT) if Acct < 120ms | |
| 4 x(PR Vmax)2 + estimated RA pressure | |
| TR PGmean + estimated RA pressure |
Examples of severe pulmonary hypertension[1]
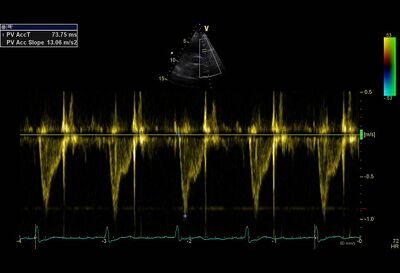
|
Video |
| Short AccT with "systolic notch" | Flattened septum |
|---|---|
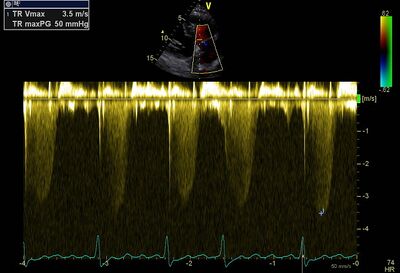
|
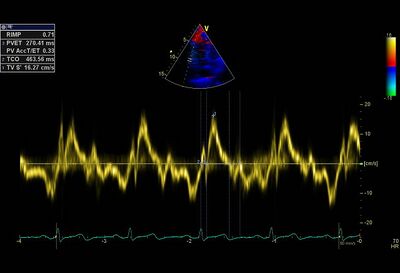
|
| Increased Systolic PA pressure | Increased MPI, extension of isovolumetric times |