Tumors: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
*The second most common primary cardiac tumor. | *The second most common primary cardiac tumor. | ||
*Location: Almost always ventricular (septal or apical). | *Location: Almost always ventricular (septal or apical). | ||
Size: ± 10cm. | *Size: ± 10cm. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Papillary fibroelastoma | |Papillary fibroelastoma | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Malignant tumors== | ==Malignant tumors== | ||
Primary malignant tumors are very rare. The most common malignant cardiac tumors are secondary tumors derived from primary diseases (see below). 3% of all patients with cancer receive cardiac metastases through the four " pathways": direct infiltration, haematogenically (through blood), lymph vessels (VCI, pulmonary veins). Malignant tumors have a poor prognosis: In malignant tumors the major risk is of the malignancy itself. | Primary malignant tumors are very rare. The most common malignant cardiac tumors are secondary tumors derived from primary diseases (see table below). 3% of all patients with cancer receive cardiac metastases through the four "pathways": direct infiltration, haematogenically (through blood), lymph vessels (VCI, pulmonary veins). Malignant tumors have a poor prognosis: In malignant tumors the major risk is of the malignancy itself. | ||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" width="600px" | {| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" width="600px" | ||
| Line 103: | Line 104: | ||
|- | |- | ||
!left atrium | !left atrium | ||
| | |||
*Myxoma | |||
*Thrombus | |||
*Papillary fibroelastoma | |||
*Sarcoma | |||
|- | |- | ||
!Eight atrium | !Eight atrium | ||
| | |||
*Myxoma | |||
*Angiosarcoma | |||
*Lymphoma | |||
*Thrombus | |||
*Papillary fibroelastoma | |||
|- | |- | ||
!Left ventricular | !Left ventricular | ||
| | |||
*Fibroma | |||
*Rhabdomyoma | |||
Papillary | *Thrombus | ||
*Papillary fibroelastoma | |||
|- | |- | ||
!Right ventricle | !Right ventricle | ||
| | |||
*Fibroma | |||
*Rhabdomyoma | |||
*Angiosarcoma | |||
*Lymphoma | |||
*Thrombus | |||
*Papillary fibroelastoma | |||
|} | |} | ||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" width="600px" | {| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" width="600px" | ||
|- | |||
|+ Examples<cite>1</cite> | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Video | |Video | ||
| | |align="center"|[[Image:TrombusRA.jpg|300px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
! | !Myxoma LA | ||
! | !Thrombus RA | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Video | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
!Vegetation TV | !Vegetation TV | ||
! | |||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:53, 7 February 2014
Benign tumors
Usually, a cardiac tumor is benign in nature. A benign tumor has a good prognosis at thrombi. Vegetations and some tumors are the most at risk embolism.
| (Primary) Benign tumors | |
|---|---|
| Myxoma |
|
| Fibroma |
|
| Papillary fibroelastoma |
|
| Lipoma |
|
| Rhabdomyoma |
|
| Hemangioma |
|
| Lambl's excrescences |
|
| Cysts |
|
| Thrombi |
|
Malignant tumors
Primary malignant tumors are very rare. The most common malignant cardiac tumors are secondary tumors derived from primary diseases (see table below). 3% of all patients with cancer receive cardiac metastases through the four "pathways": direct infiltration, haematogenically (through blood), lymph vessels (VCI, pulmonary veins). Malignant tumors have a poor prognosis: In malignant tumors the major risk is of the malignancy itself.
| Primary malignant tumors | |
|---|---|
| Angiosarcoma |
|
| Rhabdomyosarcoma |
|
| Mesothelioma |
|
| Secondary malignant tumors | |
| Metastases |
|
| Location | Tumor |
|---|---|
| left atrium |
|
| Eight atrium |
|
| Left ventricular |
|
| Right ventricle |
|
| Video | 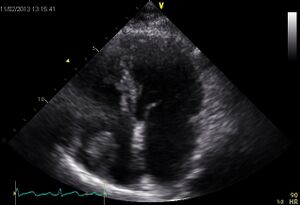
|
| Myxoma LA | Thrombus RA |
|---|---|
| Video | |
| Vegetation TV |
References
<biblio>
- 1 Hamer, J.P.M. “Cardiale massa’s”, in: Hamer/Pieper, ‘Praktische echocardiografie’, (2006), 1e druk 2e oplage, Houten, Bohn Stafleu van loghum, p.198-207.
</biblio>