Cardiomyopathy: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Click [http://www.cardiogenetica.nl/index.php?menuID=2 '''here'''] for detailed information on various cardiomyopathy | Click [http://www.cardiogenetica.nl/index.php?menuID=2 '''here'''] for detailed information on various cardiomyopathy. | ||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | {| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | ||
|+ Listed below are the main disorders and their characteristics with examples.<cite>1</cite> | |||
|- | |- | ||
!Condition | !Condition | ||
!Features | !Features | ||
!Example | !Example | ||
| Line 97: | Line 98: | ||
!Apical hypertrophy | !Apical hypertrophy | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Non - compaction cardiomyopathy (NCCMP) | !rowspan="4" valign="top"|Non-compaction cardiomyopathy (NCCMP) | ||
|rowspan="4" valign="top"| | |||
*LV wall has a spongy appearance. | |||
Jenni criteria (Heart 2007). | *Jenni criteria (Heart 2007). | ||
Also called insulated non compaction of the ventricular myocardium (INVM), is a rare form of congenital heart disease in which the tissue of the ventricular myocardium is constructed in terms of texture | *Also called insulated non compaction of the ventricular myocardium (INVM), it is a rare form of congenital heart disease in which the tissue of the ventricular myocardium is not well constructed in terms of texture. | ||
*After HCM DCM, it is the most common cause of primary cardiomyopathy in children. | |||
It is a congenital defect, which occurs in the 20th week of pregnancy. | *It is a congenital defect, which occurs in the 20th week of pregnancy. | ||
The condition is expressed by heart failure, arrhythmias, and an increased risk of thrombus formation. | *The condition is expressed by heart failure, arrhythmias, and an increased risk of thrombus formation. | ||
The disorder often manifests itself later in life and has a high mortality rate due to heart failure and arrhythmias. | *The disorder often manifests itself later in life and has a high mortality rate due to heart failure and arrhythmias. | ||
|[[Image:NCCMP02.jpg|400px]] | |||
NCCMP with crypts and apical midventriculair | |- | ||
!NCCMP with crypts and apical midventriculair | |||
NCCCMP on PSax | |- | ||
|Video | |||
|- | |||
!NCCCMP on PSax | |||
Stiffened myocardium. | |- | ||
This form comes after at least 1 and is usually associated with storage diseases, such as sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, and the like. | !rowspan="2" valign="top"|Restrictive cardiomyopathy | ||
Preserved systolic LVF. LV is not dilated. | |rowspan="2" valign="top"| | ||
Diastolic dysfunction (see fig.) | *Stiffened myocardium. | ||
LV and RV may be hypertrophied. | *This form comes after at least 1 and is usually associated with storage diseases, such as sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, and the like. | ||
Dilated atria and VCI. | *Preserved systolic LVF. LV is not dilated. | ||
Pulmonary hypertension. | *Diastolic dysfunction (see fig.) | ||
Myocardial echo during and amyloidosis speckled | *LV and RV may be hypertrophied. | ||
*Dilated atria and VCI. | |||
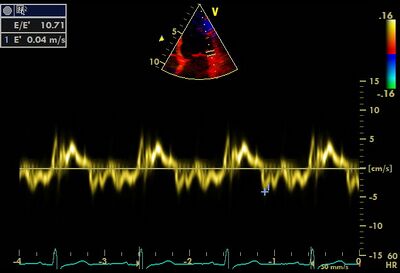
Abnormally low É in restrictive | *Pulmonary hypertension. | ||
Tako- tsubo cardiomyopathy | *Myocardial echo during and amyloidosis speckled | ||
|[[Image:Restrcmp.jpg|400px]] | |||
Apical ballooning, | |- | ||
!Abnormally low É in restrictive cardiomyopathy | |||
Is more common in women than in men, the average age of 62 to 75 years. | |- | ||
!rowspan="2" valign="top"|Tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy | |||
Also called "broken heart syndrome" or " Stress CMP " | |rowspan="2" valign="top"| | ||
LV | *Takotsubo is named after the ceramic pots used to trap octopus in Japan. | ||
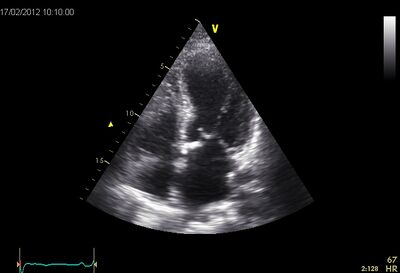
*Apical ballooning, akinetic of the apex. This gives the LV the octupus trap shape. | |||
Apical ballooning | *Manifests itself as an acute myocardial infarction with ST elevations, however, no significant coronary artery disease. | ||
*Is more common in women than in men, the average age of 62 to 75 years. | |||
*Stress induced, is triggered by an acute illness or intense emotional or physical stress | |||
*Also called "broken heart syndrome" or "Stress CMP". | |||
*LV normalizes in a few days to several weeks. | |||
|[[Image:TakoTsubo01.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |||
!Apical ballooning | |||
|} | |} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
#1 [http://www.uptodate.com/contents/echocardiographic-recognition-of-cardiomyopathies?source=search_result&search=cardiomyopathy+echo&selectedTitle=1~150| Echocardiographic recognition of cardiomyopathies] | #1 [http://www.uptodate.com/contents/echocardiographic-recognition-of-cardiomyopathies?source=search_result&search=cardiomyopathy+echo&selectedTitle=1~150| Echocardiographic | ||
#2 recognition of cardiomyopathies] | |||
#3 [https://vetocorleone.com/download-idn-poker/ Download IDN Poker APk] | |||
#4 [https://vetocorleone.com/deposit-idn-poker/ Deposit IDNPoker Terbaru] | |||
#5 [https://vetocorleone.com/daftar-idn-poker/ Daftar IDN Poker Online] | |||
#6 [https://vetocorleone.com/ IDN Poker] | |||
#7 [https://daftar-idn-poker88.wildapricot.org/ IDN Poker] | |||
#8 [https://togelonlineku3.wildapricot.org/ Togel Hongkong] | |||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
Latest revision as of 04:33, 15 June 2021
Cardiomyopathy (CMP) is a collective term for various diseases of the heart muscle (myocardium). For various reasons, the function of the myocardium decreased (see table). The different variants of a CMP are generally classified on the basis of echocardiographic characteristics.
| LV function decline in most common cardiomyopathy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Systolic function | Diastolic Function | |
| Dilated CMP | ↓ | =/↓ |
| Hypertrophic CMP | ↑ | ↓ |
| Restrictive CMP | = | ↓ |
Click here for detailed information on various cardiomyopathy.
| Condition | Features | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Arrythmogene right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) |
|
Video |
| Echodense RV free wall for suspected ARVC | ||
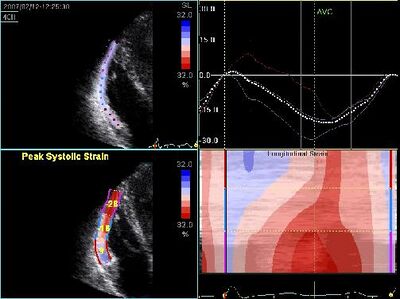
| ||
| Decreased RV strain in ARVC | ||
| Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) |
|
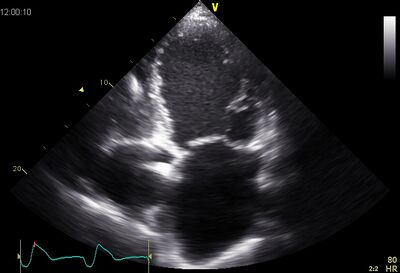
|
| Dilated LV on AP4CH | ||
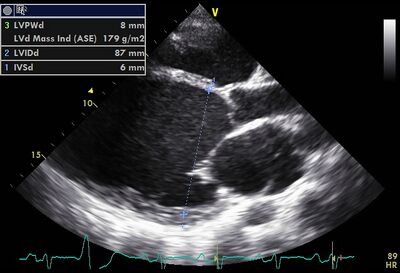
| ||
| Dilated LV on PLAX | ||
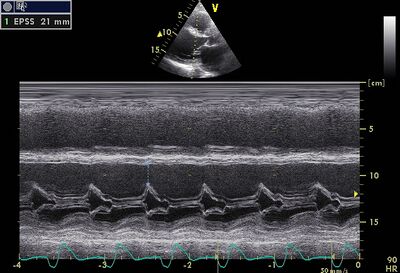
| ||
| EPSS is a useful measurement to follow up DCM | ||
| Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) |
|
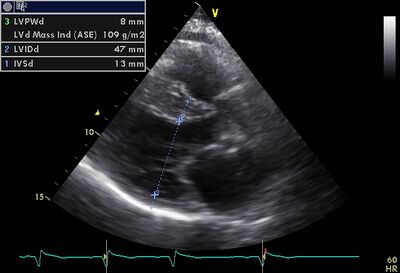
|
| Asymmetric hypertrophy | ||
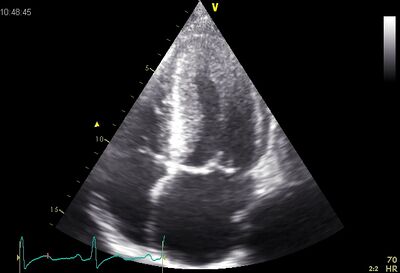
| ||
| Symmetrical hypertrophy | ||
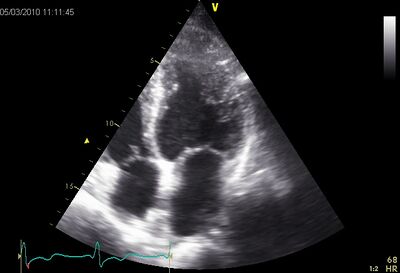
| ||
| Apical hypertrophy | ||
| Non-compaction cardiomyopathy (NCCMP) |
|
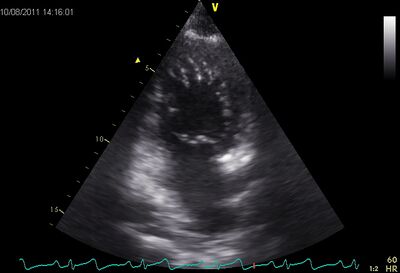
|
| NCCMP with crypts and apical midventriculair | ||
| Video | ||
| NCCCMP on PSax | ||
| Restrictive cardiomyopathy |
|
|
| Abnormally low É in restrictive cardiomyopathy | ||
| Tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy |
|
|
| Apical ballooning |
References
-
recognition of cardiomyopathies]