Normal Values of TTE: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1,254: | Line 1,254: | ||
#ASEDF pmid=19187853 | #ASEDF pmid=19187853 | ||
#Hamer isbn=9031362352 | #Hamer isbn=9031362352 | ||
</ | </biblio> | ||
Revision as of 19:24, 11 December 2016
Below an up-to-date list of echocardiographic normal values.
Left Ventricle
Left Ventricular Systolic Function
| Women | Men | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference range | Mildly abnormal | Moderately abnormal | Severely abnormal | Reference range | Mildly abnormal | Moderately abnormal | Severely abnormal | |
| Linear method | ||||||||
| Endocardial fractional shortening, % | 27–45 | 22–26 | 17–21 | ≤16 | 25–43 | 20–24 | 15–19 | ≤14 |
| Midwall fractional shortening, % | 15–23 | 13–14 | 11–12 | ≤10 | 14–22 | 12–13 | 10–11 | ≤10 |
| 2D Method | ||||||||
| Ejection fraction, % | ≥55 | 45–54 | 30–44 | <30 | ≥55 | 45–54 | 30–44 | <30 |
| ||||||||
Left Ventricular Diastolic Function

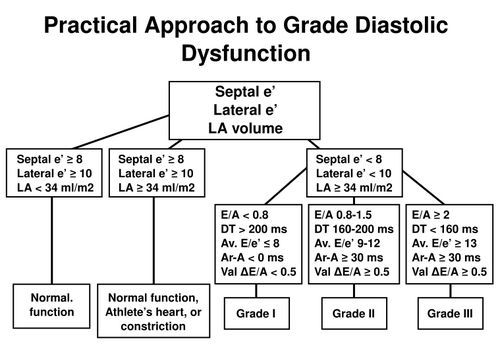
Practical approach to LV diastolic function grading. Ater [1]
| Age group (y) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement | 16-20 | 21-40 | 41-60 | >60 |
| IVRT (ms) | 50 ± 9 (32-68) | 67 ± 8 (51-83) | 74 ± 7 (60-88) | 87 ± 7 (73-101) |
| E/A ratio | 1.88 ± 0.45 (0.98-2.78) | 1.53 ± 0.40 (0.73-2.33) | 1.28 ± 0.25 (0.78-1.78) | 0.96 ± 0.18 (0.6-1.32) |
| DT (ms) | 142 ± 19 (104-180) | 166 ± 14 (138-194) | 181 ± 19 (143-219) | 200 ± 29 (142-258) |
| A duration (ms) | 113 ± 17 (79-147) | 127 ± 13 (101-153) | 133 ± 13 (107-159) | 138 ± 19 (100-176) |
| PV S/D ratio | 0.82 ± 0.18 (0.46-1.18) | 0.98 ± 0.32 (0.34-1.62) | 1.21 ± 0.2 (0.81-1.61) | 1.39 ± 0.47 (0.45-2.33) |
| PV Ar (cm/s) | 16 ± 10 (1-36) | 21 ± 8 (5-37) | 23 ± 3 (17-29) | 25 ± 9 (11-39) |
| PV Ar duration (ms) | 66 ± 39 (1-144) | 96 ± 33 (30-162) | 112 ± 15 (82-142) | 113 ± 30 (53-173) |
| Septal e´ (cm/s) | 14.9 ± 2.4 (10.1-19.7) | 15.5 ± 2.7 (10.1-20.9) | 12.2 ± 2.3 (7.6-16.8) | 10.4 ± 2.1 (6.2-14.6) |
| Septal e´/a´ ratio | 2.4∗ | 1.6 ± 0.5 (0.6-2.6) | 1.1 ± 0.3 (0.5-1.7) | 0.85 ± 0.2 (0.45-1.25) |
| Lateral e´ (cm/s) | 20.6 ± 3.8 (13-28.2) | 19.8 ± 2.9 (14-25.6) | 16.1 ± 2.3 (11.5-20.7) | 12.9 ± 3.5 (5.9-19.9) |
| Lateral e´/a´ ratio | 3.1∗ | 1.9 ± 0.6 (0.7-3.1) | 1.5 ± 0.5 (0.5-2.5) | 0.9 ± 0.4 (0.1-1.7) |
| ||||
Left Ventricular Mass and Geometry
| Women | Men | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference range |
Mildly abnormal |
Moderately abnormal |
Severely abnormal |
Reference range |
Mildly abnormal |
Moderately abnormal |
Severely abnormal | |
| Linear Method | ||||||||
| LV mass, g | 67–162 | 163–186 | 187–210 | ≥211 | 88–224 | 225–258 | 259–292 | ≥293 |
| LV mass/BSA, g/m2 | 43–95 | 96–108 | 109–121 | ≥122 | 49–115 | 116–131 | 132–148 | ≥149 |
| LV mass/height, g/m | 41–99 | 100–115 | 116–128 | ≥129 | 52–126 | 127–144 | 145–162 | ≥163 |
| LV mass/height2, g/m2 | 18–44 | 45–51 | 52–58 | ≥59 | 20–48 | 49–55 | 56–63 | ≥64 |
| Relative wall thickness, cm | 0.22–0.42 | 0.43–0.47 | 0.48–0.52 | ≥0.53 | 0.24–0.42 | 0.43–0.46 | 0.47–0.51 | ≥0.52 |
| Septal thickness, cm | 0.6–0.9 | 1.0–1.2 | 1.3–1.5 | ≥1.6 | 0.6–1.0 | 1.1–1.3 | 1.4–1.6 | ≥1.7 |
| Posterior wall thickness, cm | 0.6–0.9 | 1.0–1.2 | 1.3–1.5 | ≥1.6 | 0.6–1.0 | 1.1–1.3 | 1.4–1.6 | ≥1.7 |
| 2D Method | ||||||||
| LV mass, g | 66–150 | 151–171 | 172–182 | >193 | 96–200 | 201–227 | 228–254 | >255 |
| LV mass/BSA, g/m2 | 44–88 | 89–100 | 101–112 | ≥113 | 50–102 | 103–116 | 117–130 | ≥131 |
| ||||||||
Left Ventricular Size
| Women | Men | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference range |
Mildly abnormal |
Moderately abnormal |
Severely abnormal |
Reference range |
Mildly abnormal |
Moderately abnormal |
Severely abnormal | |
| LV dimension | ||||||||
| LV diastolic diameter | 3.9–5.3 | 5.4–5.7 | 5.8–6.1 | ≥6.2 | 4.2–5.9 | 6.0–6.3 | 6.4–6.8 | ≥6.9 |
| LV diastolic diameter/BSA, cm/m2 | 2.4–3.2 | 3.3–3.4 | 3.5–3.7 | ≥3.8 | 2.2–3.1 | 3.2–3.4 | 3.5–3.6 | ≥3.7 |
| LV diastolic diameter/height, cm/m | 2.5–3.2 | 3.3–3.4 | 3.5–3.6 | ≥3.7 | 2.4–3.3 | 3.4–3.5 | 3.6–3.7 | ≥3.8 |
| LV volume | ||||||||
| LV diastolic volume, mL | 56–104 | 105–117 | 118–130 | ≥131 | 67–155 | 156–178 | 179–201 | ≥201 |
| LV diastolic volume/BSA, mL/m2 | 35–75 | 76–86 | 87–96 | ≥97 | 35–75 | 76–86 | 87–96 | ≥97 |
| LV systolic volume, mL | 19–49 | 50–59 | 60–69 | ≥70 | 22–58 | 59–70 | 71–82 | ≥83 |
| LV systolic volume/BSA, mL/m2 | 12–30 | 31–36 | 37–42 | ≥43 | 12–30 | 31–36 | 37–42 | ≥43 |
| ||||||||
Right Ventricle
Right Ventricular and Pulmonary Artery Size
| Reference range | Mildly abnormal | Moderately abnormal | Severely abnormal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RV dimensions | ||||
| Basal RV diameter (RVD 1), cm | 2.0–2.8 | 2.9–3.3 | 3.4–3.8 | ≥3.9 |
| Mid-RV diameter (RVD 2), cm | 2.7–3.3 | 3.4–3.7 | 3.8–4.1 | ≥4.2 |
| Base-to-apex length (RVD 3), cm | 7.1–7.9 | 8.0–8.5 | 8.6–9.1 | ≥9.2 |
| RVOT diameters | ||||
| Above aortic valve (RVOT 1), cm | 2.5–2.9 | 3.0–3.2 | 3.3–3.5 | ≥3.6 |
| Above pulmonic valve (RVOT 2), cm | 1.7–2.3 | 2.4–2.7 | 2.8–3.1 | ≥3.2 |
| PA diameter | ||||
| Below pulmonic valve (PA 1), cm | 1.5–2.1 | 2.2–2.5 | 2.6–2.9 | ≥3.0 |
| ||||
Right Ventricular Size and Function
| Reference range | Mildly abnormal | Moderately abnormal | Severely abnormal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RV diastolic area, cm2 | 11–28 | 29–32 | 33–37 | ≥38 | |
| RV systolic area, cm2 | 7.5–16 | 17–19 | 20–22 | ≥23 | |
| RV fractional area change, % | 32–60 | 25–31 | 18–24 | ≤17 | |
| TAPSE, (cm) | 1.5-2.0[2] | 1.3-1.5[4] | 1.0-1.2[4] | <1.0[4] | |
| |||||
Atria
Left Atrial Dimensions / Volumes
| Women | Men | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference range | Mildly abnormal | Moderately abnormal | Severely abnormal | Reference range | Mildly abnormal | Moderately abnormal | Severely abnormal | |
| Atrial dimensions
| ||||||||
| LA diameter, cm | 2.7–3.8 | 3.9–4.2 | 4.3–4.6 | ≥4.7 | 3.0–4.0 | 4.1–4.6 | 4.7–5.2 | ≥5.2 |
| LA diameter/BSA, cm/m2 | 1.5–2.3 | 2.4–2.6 | 2.7–2.9 | ≥3.0 | 1.5–2.3 | 2.4–2.6 | 2.7–2.9 | ≥3.0 |
| RA minor-axis dimension, cm | 2.9–4.5 | 4.6–4.9 | 5.0–5.4 | ≥5.5 | 2.9–4.5 | 4.6–4.9 | 5.0–5.4 | ≥5.5 |
| RA minor-axis dimension/BSA, cm/m2 | 1.7–2.5 | 2.6–2.8 | 2.9–3.1 | ≥3.2 | 1.7–2.5 | 2.6–2.8 | 2.9–3.1 | ≥3.2 |
| Atrial area | ||||||||
| LA area, cm2 | ≤20 | 20–30 | 30–40 | >40 | ≤20 | 20–30 | 30–40 | >40 |
| Atrial volumes | ||||||||
| LA volume, mL | 22–52 | 53–62 | 63–72 | ≥73 | 18–58 | 59–68 | 69–78 | ≥79 |
| LA volume/BSA, mL/m2 | 22 ± 6 | 29–33 | 34–39 | ≥40 | 22 ± 6 | 29–33 | 34–39 | ≥40 |
| ||||||||
Left Atrial Pressure

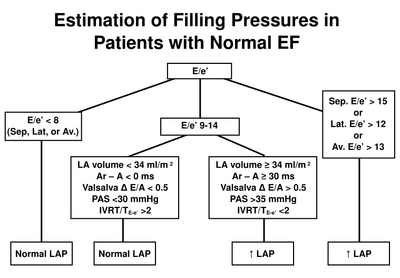
Estimation of left atrial pressure in normal LVEF. After [1]

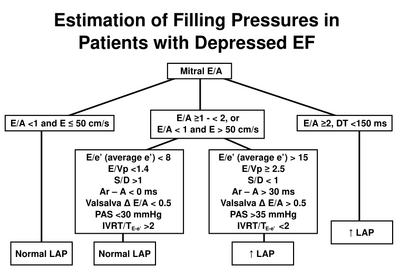
Estimation of left atrial pressure in reduced LVEF. After [1]
Aortic Valve
Aortic valve stenosis - severity
| Aortic sclerosis | Mild | Moderate | Severe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aortic jet velocity (m/s) | ≤2.5 m/s | 2.6-2.9 | 3.0-4.0 | >4.0 |
| Mean gradient (mmHg) | - | <20 (<30a) | 20-40b (30-50a) | >40b (>50a) |
| AVA (cm2) | - | >1.5 | 1.0-1.5 | <1 |
| Indexed AVA (cm2/m2) | >0.85 | 0.60-0.85 | <0.6 | |
| Velocity ratio | >0.50 | 0.25-0.50 | <0.25 | |
Aortic regurgitation - severity
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific signs for AR severity |
|
|
| |
| Supportive signs |
|
|
| |
| Quantitative parametersψ | ||||
| R Vol, ml/beat | < 30 | 30-44 | 45-59 | ≥ 60 |
| RF % | < 30 | 30-39 | 40-49 | ≥ 50 |
| EROA, cm2 | < 0.10 | 0.10-0.19 | 0.20-0.29 | ≥ 0.30 |
| ||||
Mitral Valve
Mitral regurgitation - severity
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific signs of severity |
|
|
| |
| Supportive signs |
|
|
| |
| Quantitative parametersφ | ||||
| R Vol (ml/beat) | < 30 | 30-44 | 45-59 | ≥ 60 |
| RF (%) | < 30 | 30-39 | 40-49 | ≥ 50 |
| EROA (cm2) | < 0.20 | 0.20-0.29 | 0.30-0.39 | ≥ 0.40 |
| ||||
Mitral stenosis - severity
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific findings | |||
| Valve area (cm2) | >1.5 | 1.0-1.5 | <1.0 |
| Supportive findings | |||
| Mean gradient (mmHg)a | <5 | 5-10 | >10 |
| Pulmonary artery pressure (mmHg) | <30 | 30-50 | >50 |
| |||
Mitral valve stenosis - Wilkins score
| Grade | Mobility | Thickening | Calcification | Subvalvular Thickening |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Highly mobile valve with only leaflet tips restricted | Leaflets near normal in thickness (4-5 mm) | A single area of increased echo brightness | Minimal thickening just below the mitral leaflets |
| 2 | Leaflet mid and base portions have normal mobility | Midleaflets normal, considerable thickening of margins (5-8 mm) | Scattered areas of brightness confined to leaflet margins | Thickening of chordal structures extending to one-third of the chordal length |
| 3 | Valve continues to move forward in diastole, mainly from the base | Thickening extending through the entire leaflet (5-8mm) | Brightness extending into the mid-portions of the leaflets | Thickening extended to distal third of the chords |
| 4 | No or minimal forward movement of the leaflets in diastole | Considerable thickening of all leaflet tissue (>8-10mm) | Extensive brightness throughout much of the leaflet tissue | Extensive thickening and shortening of all chordal structures extending down to the papillary muscles |
| ||||
Mitral stenosis - routine measurements
| Data element | Recording | Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Planimetry | ||
| - 2D parasternal short-axis view | - contour of the inner mitral orifice | |
| - determine the smallest orifice by scanning from apex to base | - include commissures when opened | |
| - positioning of measurement plan can be oriented by 3D echo | - in mid-diastole (use cine-loop) | |
| - lowest gain setting to visualize the whole mitral orifice | - average measurements if atrial fibrillation | |
| Mitral flow | ||
| - continuous-wave Doppler | - mean gradient from the traced contour of the diastolic mitral flow | |
| - apical windows often suitable (optimize intercept angle) | - pressure half-time from the descending sLope of the E-wave (mid-diastole slope if not linear) | |
| - adjust gain setting to obtain well-defined flow contour | - average measurements if atrial fibrillation | |
| Systolic pulmonary artery pressure | ||
| - continuous-wave Doppler | - maximum velocity of tricuspid regurgitant flow | |
| - multiple acoustic windows to optimize intercept angle | - estimation of right atrial pressure according to inferior vena cava diameter | |
| Valve anatomy | ||
|
- parasternal short-axis view | ||
|
- valve thickness (maximum and heterogeneity) | ||
|
- parasternal long-axis view | ||
|
- valve thickness | ||
| - apical two-chamber view | ||
| - subvalvular apparatus (chordal thickening, fusion, or shortening) | ||
|
Detail each component and summarize in a score | ||
Tricuspid Valve
Tricuspid regurgitation - severity
| Parameter | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tricuspid valve | Usually normal | Normal or abnormal | Abnormal/Flail leaflet/Poor coaptation |
| RV/RA/IVC size | Normal∗ | Normal or dilated | Usually dilated∗∗ |
| Jet area-central jets (cm2)§ | < 5 | 5-10 | > 10 |
| VC width (cm)Φ | Not defined | Not defined, but < 0.7 | > 0.7 |
| PISA radius (cm)ψ | ≤ 0.5 | 0.6-0.9 | > 0.9 |
| Jet density and contour–CW | Soft and parabolic | Dense, variable contour | Dense, triangular with early peaking |
| Hepatic vein flow† | Systolic dominance | Systolic blunting | Systolic reversal |
| |||
Tricuspid stenosis - severity
| Specific findings | |
| Mean pressure gradient | ≥5 mmHg |
| Inflow time-velocity integral | >60 cm |
| T1/2 | ≥190 ms |
| Valve area by continuity equationa | ≤1 cm2 |
| Supportive findings | |
| Enlarged right atrium ≥moderate | |
| Dilated inferior vena cava | |
| |
Pulmonary Valve
Pulmonary regurgitaion - severity
| Parameter | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pulmonic valve | Normal | Normal or abnormal | Abnormal |
| RV size | Normal∗ | Normal or dilated | Dilated |
| Jet size by color Doppler§ | Thin (usually < 10 mm in length) with a narrow origin | Intermediate | Usually large, with a wide origin; May be brief in duration |
| Jet density and deceleration rate –CW† | Soft; Slow deceleration | Dense; variable deceleration | Dense; steep deceleration, early termination of diastolic flow |
| Pulmonic systolic flow compared to systemic flow –PWφ | Slightly increased | Intermediate | Greatly increased |
| |||
Pulmonary stenosis - severity
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peak velocity (m/s) | <3 | 3-4 | >4 |
| Peak gradient (mmHg) | <36 | 36-64 | >64 |
Inferior Caval Vein
| CVP | IVC collaps on inspiration | IVC diameter |
|---|---|---|
| CVP 0-5 cm | total collaps | < 1.5 cm |
| CVP 5-10 cm | >50% | 1.5 to 2.5 cm |
| CVP 11-15 cm | <50% | 1.5 to 2.5 cm |
| CVP 16-20 cm | <50% | > 2.5 cm |
| CVP > 20 cm | no change | > 2.5 cm |
References
Click on the reference to link directly to the manuscript
- Nagueh SF, Appleton CP, Gillebert TC, Marino PN, Oh JK, Smiseth OA, Waggoner AD, Flachskampf FA, Pellikka PA, and Evangelista A. Recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2009 Feb;22(2):107-33. DOI:10.1016/j.echo.2008.11.023 |
- Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, Picard MH, Roman MJ, Seward J, Shanewise J, Solomon S, Spencer KT, St John Sutton M, Stewart W, American Society of Echocardiography's Nomenclature and Standards Committee, Task Force on Chamber Quantification, American College of Cardiology Echocardiography Committee, American Heart Association, and European Association of Echocardiography, European Society of Cardiology. Recommendations for chamber quantification. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2006 Mar;7(2):79-108. DOI:10.1016/j.euje.2005.12.014 |
- Foale R, Nihoyannopoulos P, McKenna W, Kleinebenne A, Nadazdin A, Rowland E, and Smith G. Echocardiographic measurement of the normal adult right ventricle. Br Heart J. 1986 Jul;56(1):33-44. DOI:10.1136/hrt.56.1.33 |
- ISBN:9031362352
- ISBN:0812112075
- Baumgartner H, Hung J, Bermejo J, Chambers JB, Evangelista A, Griffin BP, Iung B, Otto CM, Pellikka PA, Quiñones M, American Society of Echocardiography, and European Association of Echocardiography. Echocardiographic assessment of valve stenosis: EAE/ASE recommendations for clinical practice. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2009 Jan;22(1):1-23; quiz 101-2. DOI:10.1016/j.echo.2008.11.029 |
- Vahanian A, Baumgartner H, Bax J, Butchart E, Dion R, Filippatos G, Flachskampf F, Hall R, Iung B, Kasprzak J, Nataf P, Tornos P, Torracca L, Wenink A, Task Force on the Management of Valvular Hearth Disease of the European Society of Cardiology, and ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. Guidelines on the management of valvular heart disease: The Task Force on the Management of Valvular Heart Disease of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2007 Jan;28(2):230-68. DOI:10.1093/eurheartj/ehl428 |
- Zoghbi WA, Enriquez-Sarano M, Foster E, Grayburn PA, Kraft CD, Levine RA, Nihoyannopoulos P, Otto CM, Quinones MA, Rakowski H, Stewart WJ, Waggoner A, Weissman NJ, and American Society of Echocardiography. Recommendations for evaluation of the severity of native valvular regurgitation with two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2003 Jul;16(7):777-802. DOI:10.1016/S0894-7317(03)00335-3 |
- Wilkins GT, Weyman AE, Abascal VM, Block PC, and Palacios IF. Percutaneous balloon dilatation of the mitral valve: an analysis of echocardiographic variables related to outcome and the mechanism of dilatation. Br Heart J. 1988 Oct;60(4):299-308. DOI:10.1136/hrt.60.4.299 |
- Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Chatterjee K, de Leon AC Jr, Faxon DP, Freed MD, Gaasch WH, Lytle BW, Nishimura RA, O'Gara PT, O'Rourke RA, Otto CM, Shah PM, Shanewise JS, and American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. 2008 focused update incorporated into the ACC/AHA 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to revise the 1998 guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease). Endorsed by the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Sep 23;52(13):e1-142. DOI:10.1016/j.jacc.2008.05.007 |
- ↑ ASE