Cardiomyopathy: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
*Fibrofatty degeneration of the RV . | *Fibrofatty degeneration of the RV . | ||
*Myocardial degeneration leads to RV dilation and poor RVF . | *Myocardial degeneration leads to RV dilation and poor RVF . | ||
*Ventricular fibrillation by slow conduction velocities , guide block and spatial variation in conduction velocity . | *Ventricular fibrillation by slow conduction velocities, guide block and spatial variation in conduction velocity. | ||
*Aneurysms of the RV free wall . | *Aneurysms of the RV free wall. | ||
* | *Echodense moderator band and myocardial RV free wall. | ||
*Genetic component | *Genetic component | ||
*Rare 1 : 5000 people. | *Rare 1:5000 people. | ||
|Video | |Video | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
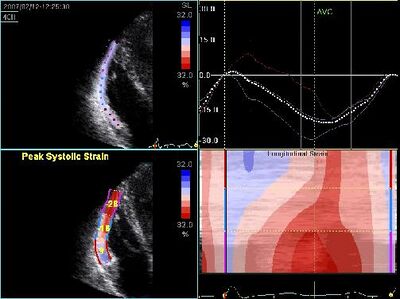
!Decreased RV strain in ARVC | !Decreased RV strain in ARVC | ||
|- | |- | ||
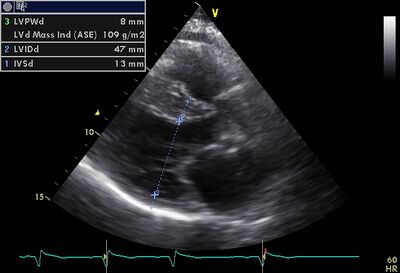
!rowspan="6" valign="top"|Dilated cardiomyopathy ( DCM ) | !rowspan="6" valign="top"|Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) | ||
|rowspan="6" valign="top"| | |rowspan="6" valign="top"| | ||
*It is the most common form of cardiomyopathy. | *It is the most common form of cardiomyopathy. | ||
*Also known as congestive cardiomyopathy | *Also known as congestive cardiomyopathy. | ||
*Poor LVF and LV dilatation. | *Poor LVF and LV dilatation. | ||
*Arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation 20-30%). | *Arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation 20-30%). | ||
*Clot formation, which may lead to thrombo-embolic complications. | *Clot formation, which may lead to thrombo-embolic complications. | ||
*Often accompanied by pulmonary hypertension, dilation of other compartments, and an insufficiency of mitral and / or tricuspid valve | *Often accompanied by pulmonary hypertension, dilation of other compartments, and an insufficiency of mitral and/or tricuspid valve | ||
*Familial DCM's common to autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive and sex-linked inheritance. | *Familial DCM's common to autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive and sex-linked inheritance. | ||
*Causes: | *Causes: | ||
**(post-) infectious: various viruses and bacteria, as the final stage of myocarditis. | **(post-) infectious: various viruses and bacteria, as at the final stage of myocarditis. | ||
**intoxication: cocaine, alcohol abuse. | **intoxication: cocaine, alcohol abuse. | ||
**iatrogenic: some chemostatica, X-ray radiation. | **iatrogenic: some chemostatica, X-ray radiation. | ||
**Metabolic: vitamin B1 deficiency. | **Metabolic: vitamin B1 deficiency. | ||
**-idiopathic: In approximately 30% of cases, no cause is found | **-idiopathic: In approximately 30% of cases, no cause is found | ||
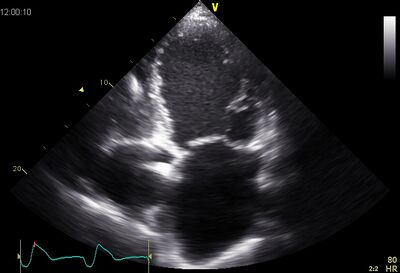
|[[Image:DCM01.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
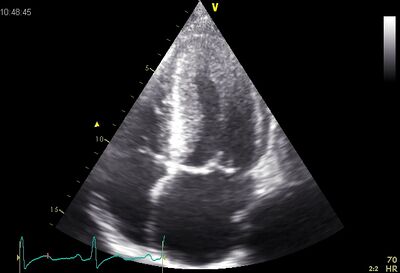
!Dilated LV on AP4CH | |||
|- | |- | ||
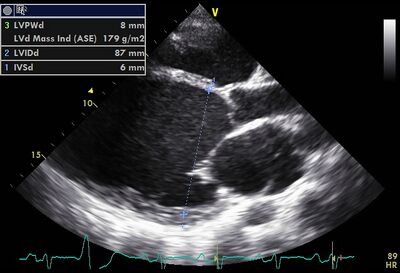
|[[Image:LVF slecht05.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
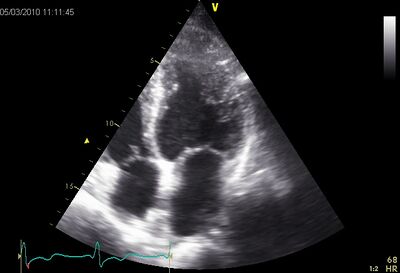
!Dilated LV on PLAX | |||
|- | |- | ||
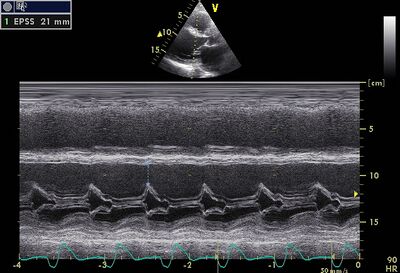
|[[Image:EPSS01.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
!EPSS is a useful measurement to follow up DCM | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | !rowspan="6" valign="top"|Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) | ||
|rowspan="6" valign="top"| | |||
*65% asymmetric hypertrophy of the myocardium, usually ventricular septum sometimes apical involvement. | |||
*35% symmetrical hypertrophy of the myocardium (not to be confused with aortic stenosis or hypertension). | |||
*Small LV lumen. | |||
*Preserved systolic LV function ( EF normal or slightly decreased) | |||
*Diastolic dysfunction. | |||
*Autosomal dominant progressive deviation from nature. | |||
*May include associated with sudden cardiac death due to ventricular fibrillation, an increased risk of thromboembolism. | |||
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy ( HCM ) | *Heart failure can be caused by the rigidity of the thickened heart muscle (diastolic heart failure), by an obstruction in the LVOT (SAM ) is associated with mitral valvular insufficiency. The course of the disease is progressive. | ||
*Occurs in persons 1:500-1000 | |||
65% | |||
35 % | |||
Small LV lumen . | |||
Preserved systolic LV function ( EF normal or slightly decreased) | |||
Diastolic dysfunction . | |||
Autosomal dominant progressive deviation from nature . | |||
May include associated with sudden cardiac death due to ventricular fibrillation , an increased risk of thromboembolism . | |||
Heart failure can be caused by the rigidity of the thickened heart muscle ( diastolic heart failure ) , by an obstruction in the LVOT (SAM ) is associated with mitral valvular insufficiency . The course of the disease is progressive . | |||
Occurs in persons 1:500-1000 | |||
asympHCM | asympHCM | ||
|[[Image:Asym.cmp1.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |||
!Asymmetric hypertrophy | |||
|- | |||
|[[Image:HCM01.jpg|400px]] | |||
Non - compaction cardiomyopathy ( NCCMP ) | |- | ||
!Symmetrical hypertrophy | |||
|- | |||
|[[Image:ApicHCM.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |||
!Apical hypertrophy | |||
|- | |||
|Non - compaction cardiomyopathy ( NCCMP ) | |||
LVwand has a spongy appearance . | LVwand has a spongy appearance . | ||
| Line 141: | Line 139: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
#1 | #1 [http://www.uptodate.com/contents/echocardiographic-recognition-of-cardiomyopathies?source=search_result&search=cardiomyopathy+echo&selectedTitle=1~150| Echocardiographic recognition of cardiomyopathies] | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
Revision as of 06:07, 25 January 2014
Cardiomyopathy (CMP) is a collective term for various diseases of the heart muscle (myocardium). For various reasons, the function of the myocardium decreased (see table). The different variants of a CMP are generally classified on the basis of echocardiographic characteristics.
| LV function decline in most common cardiomyopathy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Systolic function | Diastolic Function | |
| Dilated CMP | ↓ | =/↓ |
| Hypertrophic CMP | ↑ | ↓ |
| Restrictive CMP | = | ↓ |
Click here for detailed information on various cardiomyopathy. Listed below are the main disorders and their characteristics with examples.