Cardiomyopathy: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 130: | Line 130: | ||
!rowspan="2" valign="top"|Tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy | !rowspan="2" valign="top"|Tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy | ||
|rowspan="2" valign="top"| | |rowspan="2" valign="top"| | ||
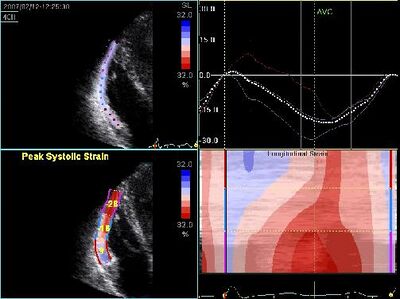
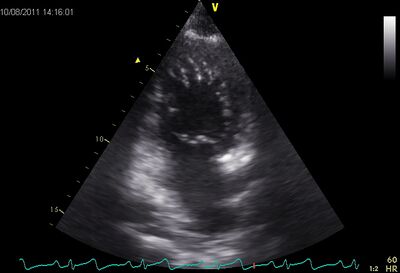
* | *Takotsubo is named after the ceramic pots used to trap octopus in Japan. | ||
Apical ballooning, | *Apical ballooning, akinetic of the apex. This gives the LV the octupus trap shape. | ||
*Manifests itself as an acute myocardial infarction with ST elevations, however, no significant coronary artery disease. | |||
Is more common in women than in men, the average age of 62 to 75 years. | *Is more common in women than in men, the average age of 62 to 75 years. | ||
*Stress induced, is triggered by an acute illness or intense emotional or physical stress | |||
Also called "broken heart syndrome" or " Stress CMP " | *Also called "broken heart syndrome" or "Stress CMP". | ||
LV | *LV normalizes in a few days to several weeks. | ||
|[[Image:TakoTsubo01.jpg|400px]] | |[[Image:TakoTsubo01.jpg|400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 06:59, 25 January 2014
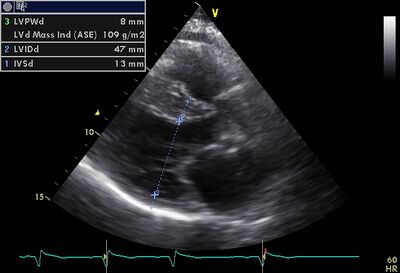
Cardiomyopathy (CMP) is a collective term for various diseases of the heart muscle (myocardium). For various reasons, the function of the myocardium decreased (see table). The different variants of a CMP are generally classified on the basis of echocardiographic characteristics.
| LV function decline in most common cardiomyopathy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Systolic function | Diastolic Function | |
| Dilated CMP | ↓ | =/↓ |
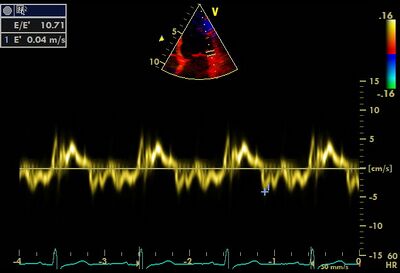
| Hypertrophic CMP | ↑ | ↓ |
| Restrictive CMP | = | ↓ |
Click here for detailed information on various cardiomyopathy. Listed below are the main disorders and their characteristics with examples.