Pulmonary Insufficiency
Quantification Pulmonaliklep insufficiency
| Slight | Moderate | Severe | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RV dimension | normal | normal/dilated | dilated |
| Density contour + CW signal | light + blunt | holds + variable | holds + steep |
| Systolic flow in pulmonary artery
decreased in decreased slightly decreased slightly |
Color Doppler signal narrow jet located under pulmonary wide level jet far into RV reaching broad retrograde jet outbound portion of pulmonary branches
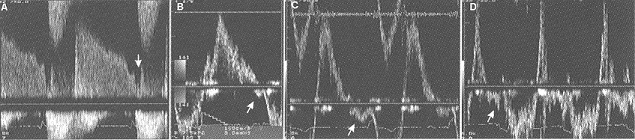
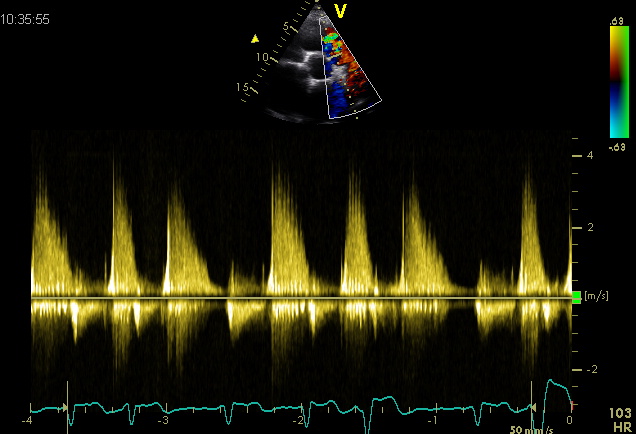
Source: European Journal of Echocardiography (2010 ) 11, 223-244 Color dopplerWith color Doppler , the degree of expansion of the jet flow back into the right ventricle can be used to quantify the degree of pulmonary insufficiency enigzinds it is most commonly used . Continuous waveAlso by continuous wave signal with an impression can be gekeregen on the severity of the pulmonary valve insufficiency. A Minimum insufficiency as seen in normal individuals : holodiastolisch signal dip by atrial contraction B Light insufficiency : holodiastolische backflow small reversal following atrial contraction only during inspiration C Moderate insufficiency : return of the return current to zero before the end of diastole to late diastolic antegrade flow in the pulmonary artery due to the atrial contraction both in inspiration and in expiration. D Severe insufficiency : short sharp backflow indicating rapid equilibration of pulmonary and RV diastolic and end-diastolic pressure with mid forward flow in the pulmonary artery . Source : Mulder B.J.M. , P. G. Pieper , Spitaels S.E.C. Congenital heart disease in adults . Bohn Stafleu of Loghum Houten / Diegem 1999 example Moderate pulmonary insufficiency References
|