Endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammatory reaction involving the heart valves. It can be divided into infectious and non -infectious causes, depending on whether there a micro-organism is present in the process. There are several manifestations of endocarditis:
- Abscess Formation
- Fistula formation
- Vegetation (most common and direct evidence of endocarditis)
| Video | Video |
| Vegetation on MV | Abscess after Aortic Prosthesis |
|---|
Non-infectious endocarditis
A non -infectious endocarditis is rare. One form of this is Libman - Sacks endocarditis mentioned and is especially common in patients with lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome. Non -infectious endocarditis can also occur in some forms of cancer.
Infectious endocarditis
The valves are not by blood, causing white blood cells, they can not get rid of infection. Normally prevents the blood that such infections can nest. Located in the heart If the valve is damaged, however, for example by rheumatic fever or after surgery, the nest much easier. Inflammatory conditions in the mouth, for example due to poor oral hygiene, are a major cause of endocarditis, because blood is in that case sometimes still occurs in contact with the outside world, and the bacteria in the mouth of the patient. In that case, usually streptococcal species found as a causative agent. If the access of the bacteria is located in the skin, such as in intravenous drug users, are often cultured staphylococci from the blood. If valve replacement surgeries have taken place and artificial valves are made, it increases the risk of endocarditis. Then, too, are often skin bacteria found.
Diagnosis of infectious endocarditis
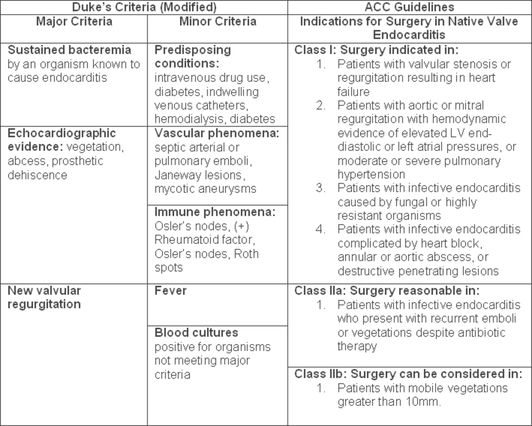
| ||
|---|---|---|
| The diagnosis of infectious endocarditis is made in the presence of at least: | ||
| Two major criteria | One major and three minor criteria | Five minor criteria. |
Therapy
The treatment consists in infective endocarditis from prolonged administration of antibiotics via the bloodstream. If there is severe damage to the heart valve, or abscess formation around the valve, or there is of complications such as embolization of infected thrombi will be passed to a surgical valve replacement.
Click here for richtlijen Endocarditis prophylaxis of the Dutch Heart Foundation
Source: European Journal of Echocardiography (2010) 11, 202-219.